Intraatrial block
It is a disorder of conduction of the impulse in the atria, most often from the right atrium to the left.
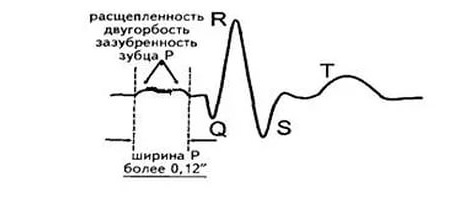
Intraatrial block does not have a characteristic clinical picture; the latter is completely determined by the underlying disease. The diagnosis is established on the basis of ECG data, on which broadening, splitting of P wave is observed. Intraatrial block is often combined with an intraventricular block.
Intraatrial block occurs in various diseases accompanied by an increasing of the atria (rheumatism, miocarditis, heart defects), as well as in disorder of innervation, when no obvious pathology of the heart is detected. Intraatrial block can be one of the electrocardiographic manifestations of sick sinus syndrome.
Intraatrial block occurs in patients with ischaemic heart disease with atherosclerotic cardiosclerosis and with myocardial infarction and also with acquired, congenital heart defects and myocarditis of various etiologies. Disorder of intraatrial conduction may occurs with an overdose of digitalis preparations, antiarrhythmics, etc. Electrolyte disorders, primarily hyperkalemia or hypokalemia, are a rare cause of its appearance.